| [1]张智海,刘忠厚,李娜,等. 中国人骨质疏松症诊断标准专家共识(第三稿•2014版)[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2014,20(9):1007-1010.[2]Kim DH, Vaccaro AR. Osteoporotic compression fractures of the spine; current options and considerations for treatment. Spine J. 2006;6(5) : 479-487. [3]Kaufman JJ, Luo G, Siffert RS. Ultrasound simulation in bone. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2008;55(6) : 1205-1208.[4]张宝鉴,薛瑞,孙润芳,等. 120例骨质疏松性脊柱骨折患者的危险因素调查分析[J]. 中医临床研究,2016,8(25):1-4.[5]Voormolen MH, Lohle PN, Juttmann JR, et al. The risk of new osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in the year after percutaneous vertebroplasty. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2006;17: 71-76[6]Lindsay R,Silverman SL,Cooper C,et al.Risk of new vertebral fracture in the year following a fracture. JAMA. 2001; 285: 320-323.[7]马海强,卢俊范,谭磊,等. 椎体成形术研究最新进展[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(18):1841-1843.[8]邱兴,杨圣,芦健民,等. 骨质疏松骨折椎体及相邻椎体骨水泥注入前后的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(17):3041-3048.[9]蒋剑锋,张烽,朱海涛. 经皮椎体成形术治疗椎体转移性肿瘤21例[J]. 南通大学学报:医学版,2008,28(5): 356-358.[10]Park CK,Allen MJ,Schoonmaker J,et al.Gelfoam as a barrier to prevent polymethylmethacrylate-induced thermal injury of the spinal cord:in vitro and in vivo studies in pigs.J Spinal Disord. 1999;12(6):496-500.[11]Tai CL, Lai PL, Lin WD,et al.Modification of Mechanical Properties, Polymerization Temperature, and Handling Time of Polymethylmethacrylate Cement for Enhancing Applicability in Vertebroplasty.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:7901562.[12]钱明,潘俊,孟斌,等. 聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥与Cortoss骨水泥生物力学性能及聚合温度比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2012,16(16): 2935-2938.[13]Kaufmann TJ,Trout AT,Kallmes DF.The effects of cement volume on clinical outcomes of percutaneous vertebroplasty. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.2006;27(9):1933-1937.[14]Phillips FM,Todd WF,Lieberman I,et al.An in vivo comparison of the potential for extravertebral cement leak after vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. Spine(PhilaPa 1976). 2002;27(19):2173-2179.[15]Lin D, Hao J, Li L,et al.Effect of Bone Cement Volume Fraction on Adjacent Vertebral Fractures after Unilateral Percutaneous Kyphoplasty.Clin Spine Surg. 2016. [Epub ahead of print][16]Cui W, Liu B, Wang L,et al.The correlation analysis of balloon volume and bone cement volume in percutaneous kyphoplasty. Chin J Surg. 2015;53(4):289-293.[17]刘志伟,姜闻博,严伟洪,等. 椎体后凸成形术骨水泥椎间盘内渗漏对邻近椎间盘的生物力学影响[J]. 江苏医药,2011,37(20):2424-2426.[18]毛海青,耿德春,朱雪松,等. 椎间盘骨水泥颗粒对人髓核细胞增殖的影响并非无足轻重[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(12):2108-2115.[19]张远华,苏艳杰,黄潮桐. 去卵巢联合糖皮质激素诱发兔骨质疏松模型的研究[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2015,33(2):204-208.[20]Bouza C, López T, Magro A,et al. Efficacy and safety of balloon kyphoplasty in the treatment of vertebral compression fractures: a systematic review. Eur Spine J. 2006;15(7):1050-1067. [21]杨丰建,林伟龙,朱炯,等. 经皮椎体成形术和经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2011,21(1):50-54.[22]董继胜,董力军,闫兵勇,等. 经皮椎体成形术和经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗老年骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折的疗效观察[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(8):748-751.[23]郑召民,李佛保.经皮椎体成形术和经皮椎体后凸成形术——问题与对策[J]. 中华医学杂志,2006,86(27):1878-1880.[24]Nakano M, Hirano N, Ishihara H,et al.Calcium phosphate cement-based vertebroplasty compared with conservative treatment for osteoporotic compression fractures: a matched case-control study.J Neurosurg Spine. 2006;4(2):110-117.[25]De Vrind HH, Wondergem J, Haveman J. Hyperthermia-induced damage to rat sciatic nerve assessed in vivo with functional methods and with electrophysiology. J Neurosci Methods. 1992; 45(3):165-174.[26]Yimin Y, Zhiwei R, Wei M, et al.Current status of percutaneous vertebroplasty and percutaneous kyphoplasty--a review. Med Sci Monit. 2013;19:826-836.[27]Fu Z, Hu X, Wu Y,et al. Is There a Dose-Response Relationship of Cement Volume With Cement Leakage and Pain Relief After Vertebroplasty? Dose Response. 2016;14(4): 1559325816682867.[28]李楠,张贵林,何达,等. 骨水泥的分布与剂量对椎体成形术疗效影响的研究[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015,30(1):66-68.[29]江晓兵,莫凌,梁德,等.骨水泥在椎体骨折线内弥散情况对椎体成形术治疗效果的影响[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2014,24(2):144-149.[30]卢昌怀,刘志军,张宏波, 等.骨水泥量及分布对椎体成形术后相邻椎体生物力学影响的三维有限元分析[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2015,21(1): 29-33.[31]Hohaus T, Ganey M, Minkus Y, et al. Cell transplantation in lumbar spine disc degeneration disease. Eur Spine J. 2008;(4):492-503.[32]Diwan AD, Parvataneni HK, Khan SN,et al.Current concepts in intervertebral disc restoration. Orthop Clin North Am. 2000;31(3): 453-464.[33]Natarajan RN, Ke JH, Andersson GB.A model to study the disc degeneration process. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994;19(3):259-265.[34]张延松,胡侦明,郝杰,等. 椎间盘退变基因治疗进展[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(7):617-620.[35]Daniels J, Binch AA, Le Maitre CL.Inhibiting IL-1 signaling pathways to inhibit catabolic processes in disc degeneration.J Orthop Res. 2017;35(1):74-85.[36]Hoyland JA,Le Maitre C,Freemont AJ. Investigation of the role of IL-1 and TNF in matrix degradation in the intervertebral disc. Rheumatology(Oxford). 2008;47(6):809-814.[37]Goupille P, Jayson MI, Valat JP,et al.Matrix metalloproteinases: the clue to intervertebral disc degeneration? Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1998;23(14):1612-1626.[38]Bonassar LJ, Frank EH, Murray JC,et al.Changes in cartilage composition and physical properties due to stromelysin degradation.Arthritis Rheum.1995;38(2):173-183.[39]Haro H, Shinomiya K, Murakami S, et al. Up-regulated expression of matrilysin and neutrophil collagenase in human herniated discs. J Spinal Disord.1999;13:245-249.[40]Le Maitre CL, Freemont AJ, Hoyland JA.Human disc degeneration is associated with increased MMP 7 expression. Biotech Histochem. 2006;81(4-6):125-131.[41]Haro H, Crawford HC, Fingleton B,et al.Matrix metalloproteinase-7- dependent release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in a model of herniated disc resorption. J Clin Invest.2000;105(2):143-150.[42]Haro H, Nishiga M, Ishii D,et al.Experimental chemonucleolysis with recombinant human matrix metalloproteinase 7 in human herniated discs and dogs.Spine J. 2014;14(7):1280-1290. [43]Matsui Y, Maeda M, Nakagami W, et al. The involvement of matrix metalloproteinases and inflammation in lumbar disc herniation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1998;23:863-868.[44]Rutges JP, Kummer JA, Oner FC, et al. Increased MMP-2 activity during intervertebral disc degeneration is correlated to MMP-14 levels. J Pathol. 2008;214:523-530. [45]Tran CM, Smith HE, Symes A, et al. Transforming growth factor (controls CCN3 expression in nucleus pulposus cells of the intervertebral disc. Arthritis Rheum. 2011; 63:3022-3031.[46]黄昊,何仕诚,冯国栋,等. 骨水泥对兔脊柱VX2肿瘤转移模型的研究[J].介入放射学杂志,2015,24(6):520-523.[47]曹建飞,张晟,叶海明,等. 骨水泥聚合反应与冷却对骨骼肌热损伤的关系[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2014,20(6):524-527.[48]Verlaan JJ, Oner FC, Verbout AJ,et al.Temperature elevation after vertebroplasty with polymethyl-methacrylate in the goat spine.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2003;67(1):581-585.[49]Belkoff SM, Molloy S.Temperature measurement during polymerization of polymethylmethacrylate cement used for vertebroplasty.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(14):1555-1559.[50]Lai PL, Tai CL, Chen LH, et al. Cement leakage causes potential thermal injury in vertebroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12: 116.[51]李宏宇,安洪,梁斌, 等. ~99Tc~m-MDP骨显像观察骨水泥阻塞兔骨干髓腔后远侧骨血流和代谢[J]. 中华核医学杂志, 2006,26(5):301-303.[52]Neidlinger-Wilke C, Würtz K, Urban JP,et al.Regulation of gene expression in intervertebral disc cells by low and high hydrostatic pressure. Eur Spine J. 2006;15 Suppl 3:S372-378.[53]王月,孔庆海,王铁铸,等. 椎体成形术后相邻椎体再骨折的临床研究[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2013,19(3):243-246.[54]杨小彬,贺宝荣,郝定均,等. 不同骨水泥量在PKP术后对相邻节段生物力学影响的有限元分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2016,31(1): 40-43.[55]徐晖,李健,程立明,等.椎体成形术后相邻椎体终板应力变化的有限元分析[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志, 2005,23(3):307-309+312.[56]樊晓光,彭长亮,武士清,等. 椎体成形术对兔手术椎体相邻椎间盘的影响[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(7):708-713.[57]田力,李庆伟,陈国武,等. 经皮椎体成形及后凸成形术对邻近椎间盘退变影响的回顾性分析研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2013,21(15): 1524-1527.[58]毛海青,耿德春,朱雪松,等. 椎间盘骨水泥颗粒对人髓核细胞增殖的影响并非无足轻重[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(12):2108-2115. |
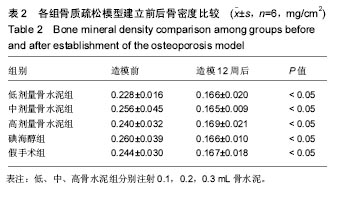
.jpg)
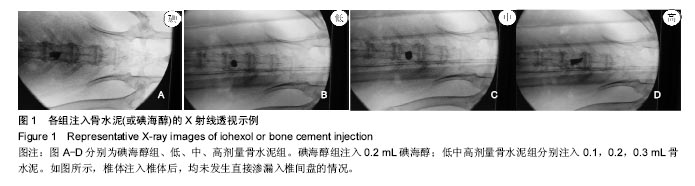

.jpg)
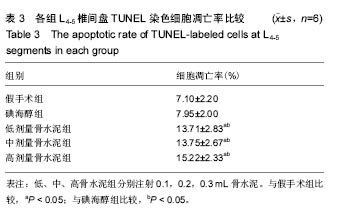
.jpg)